Artwork: Dan Nowakowski/Nicholas Taylor
Does the bacterial
flagellar engine have an automatic gearshift?
Navish Wadhwa1, Yuhai Tu2, Howard C. Berg1
1Harvard University, 2IBM Research
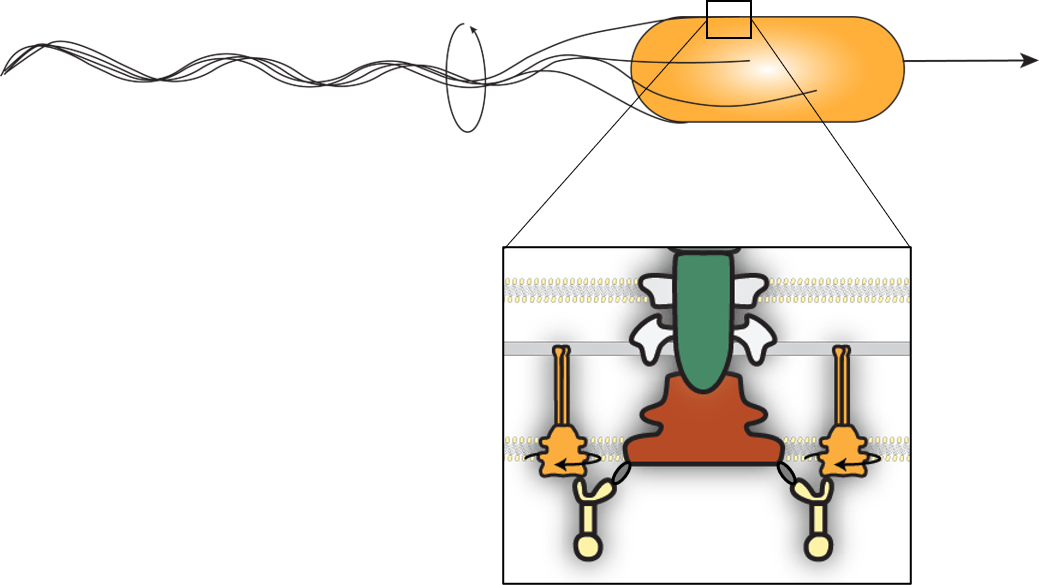
Bacteria swim by rotating helical flagella
 Slowed down 20 times
Slowed down 20 times
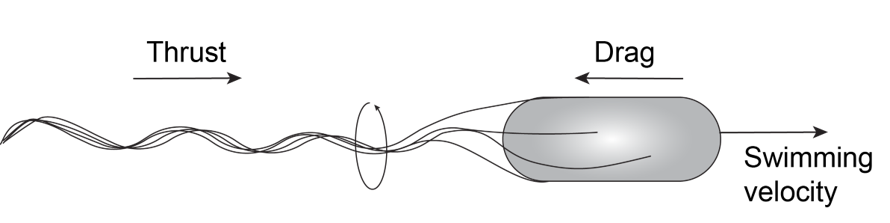
Turner et al., J. Bacteriol., 2000
...Powered by a molecular engine
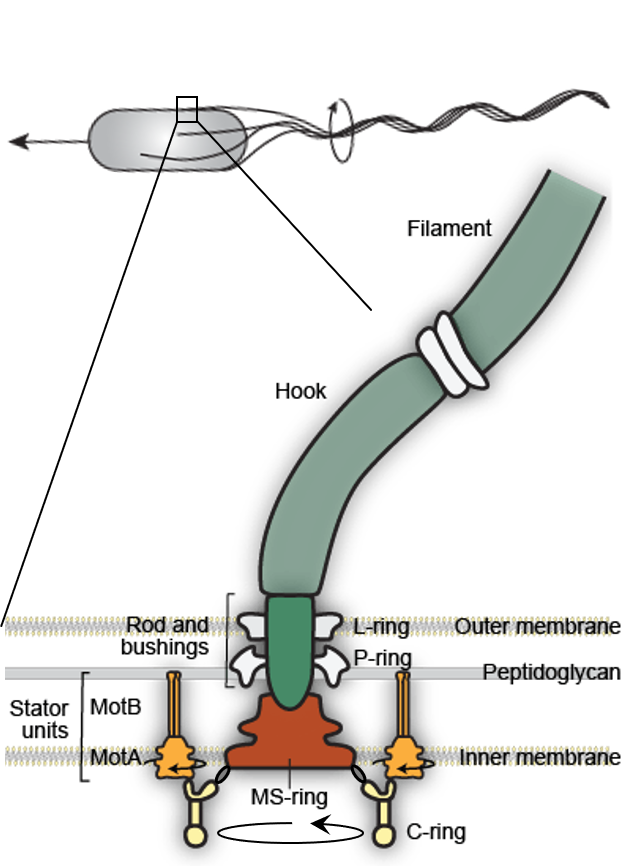
Nakamura and Minamino, Biomolecules, 2019
Santiveri et al., Cell, 2020
Leake et al., Nature, 2006
Automatic gearshift in cars allows the engine to adapt to changing terrains

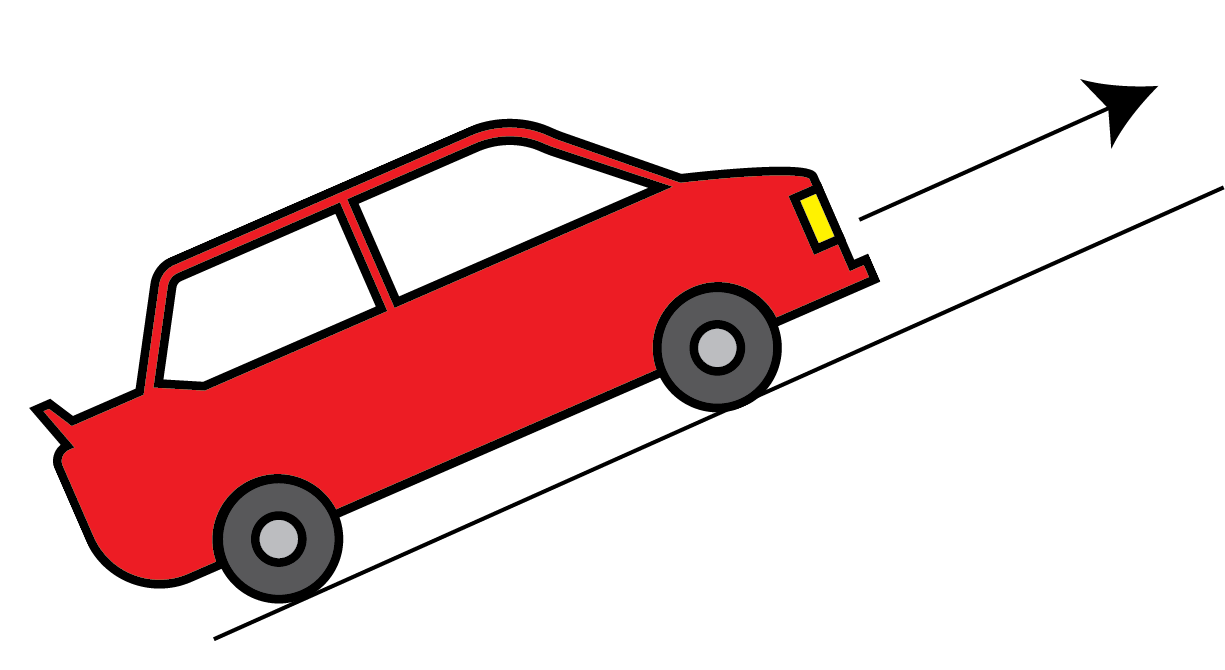
How does the bacterial flagellar engine deal with changing loads?
We used electrorotation to control motor load
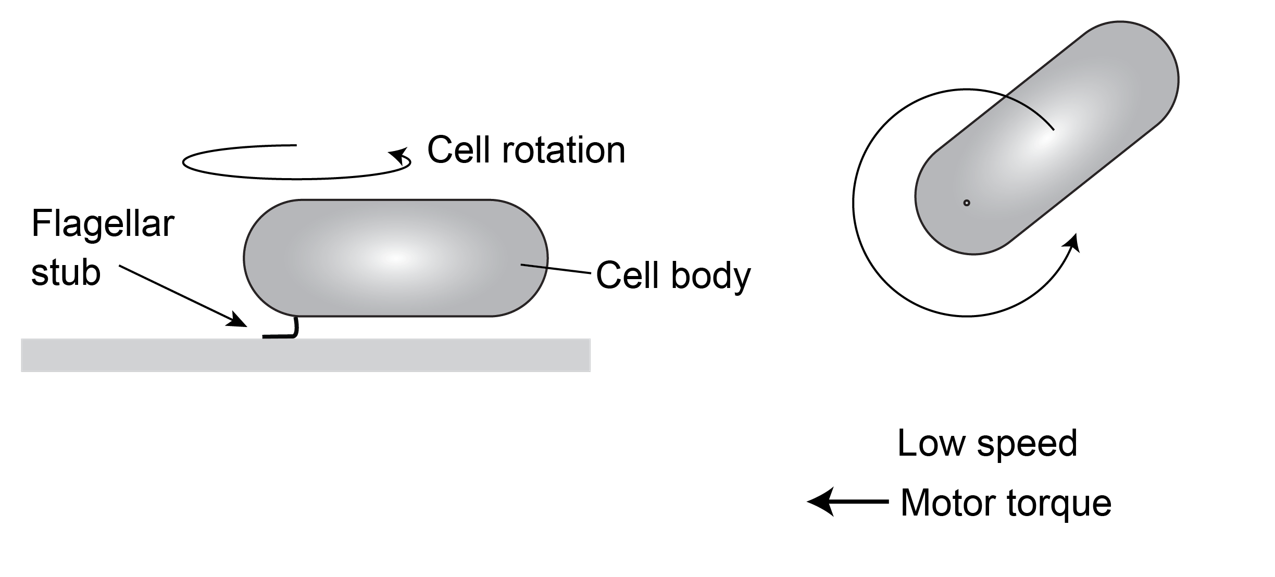
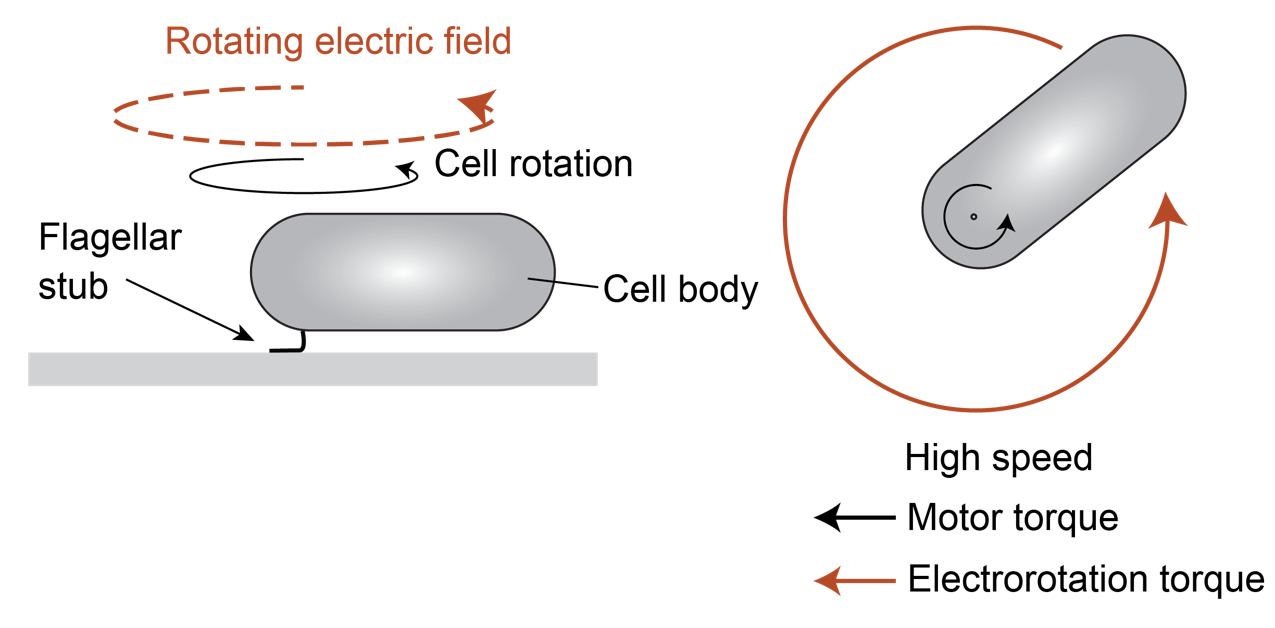
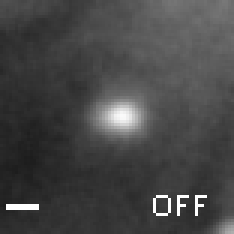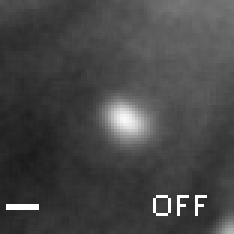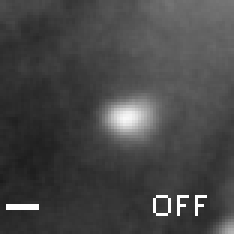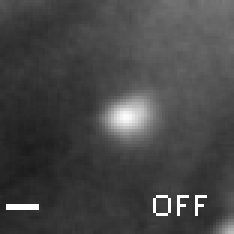
A change in load triggers stepwise changes in motor speed
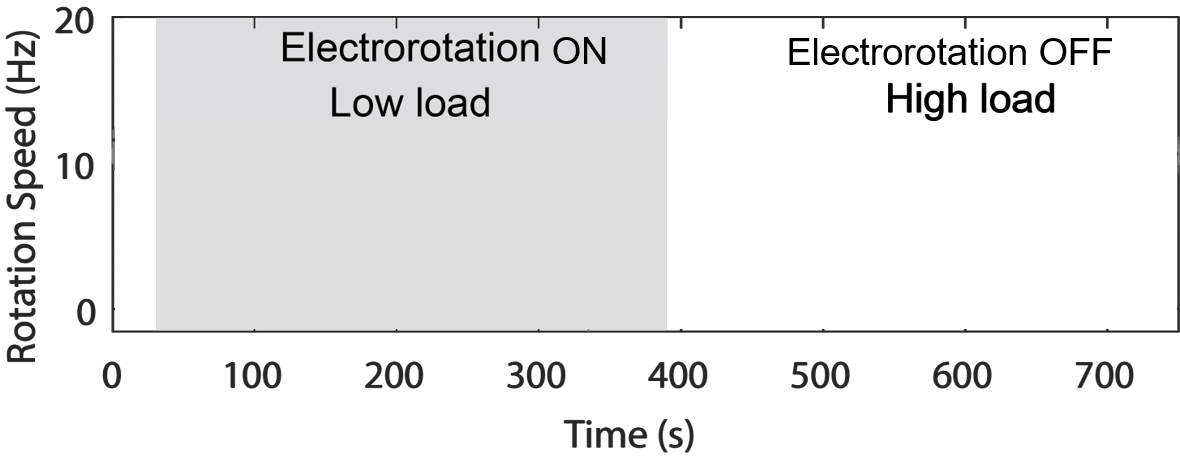
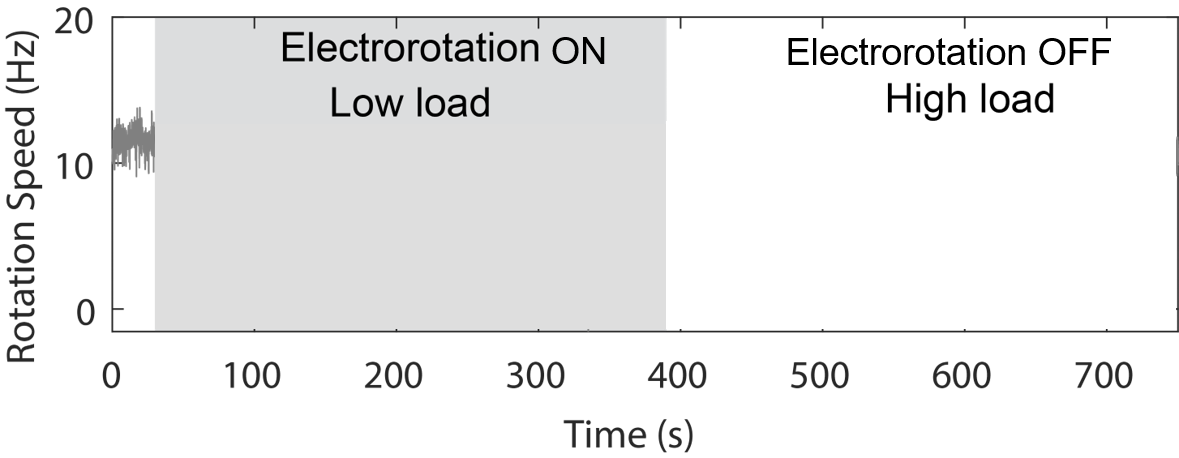
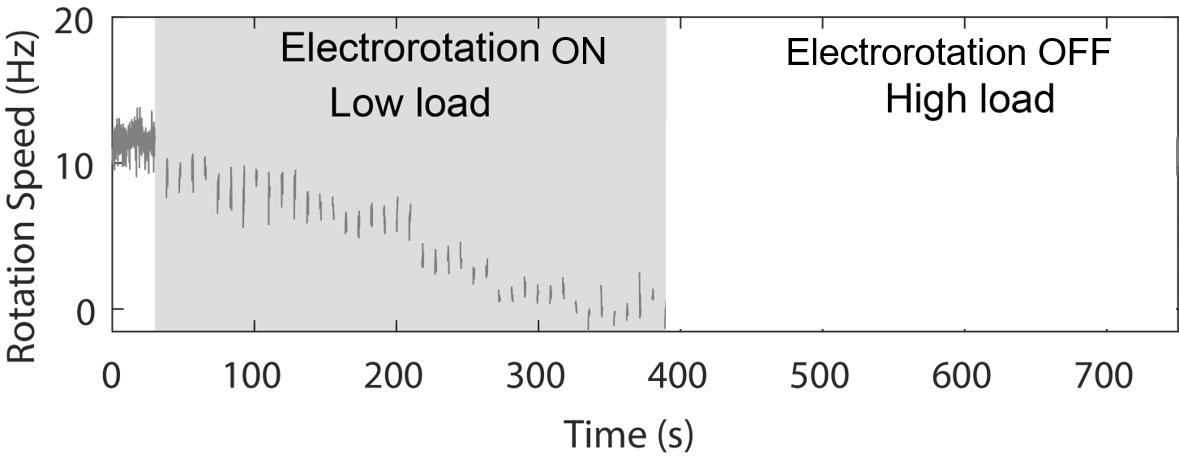
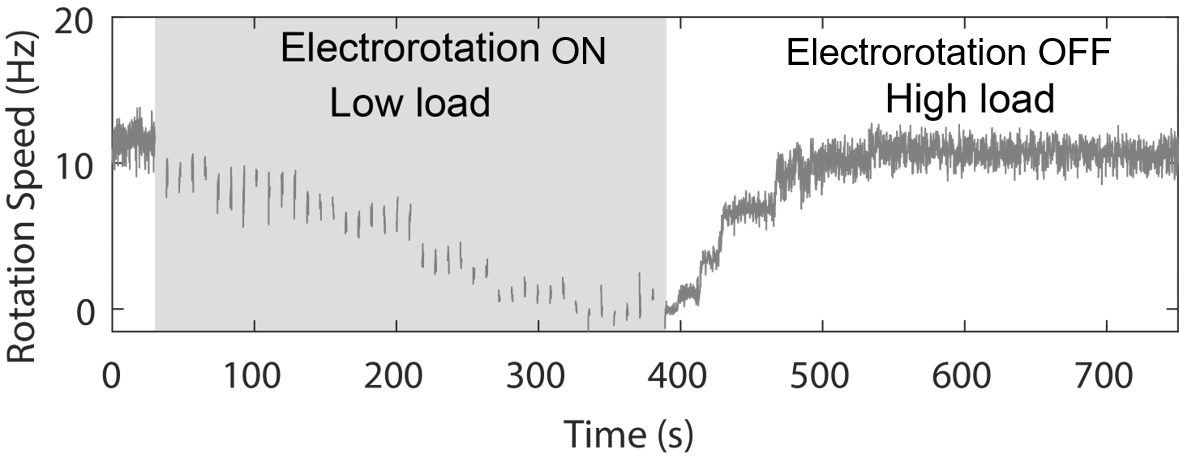
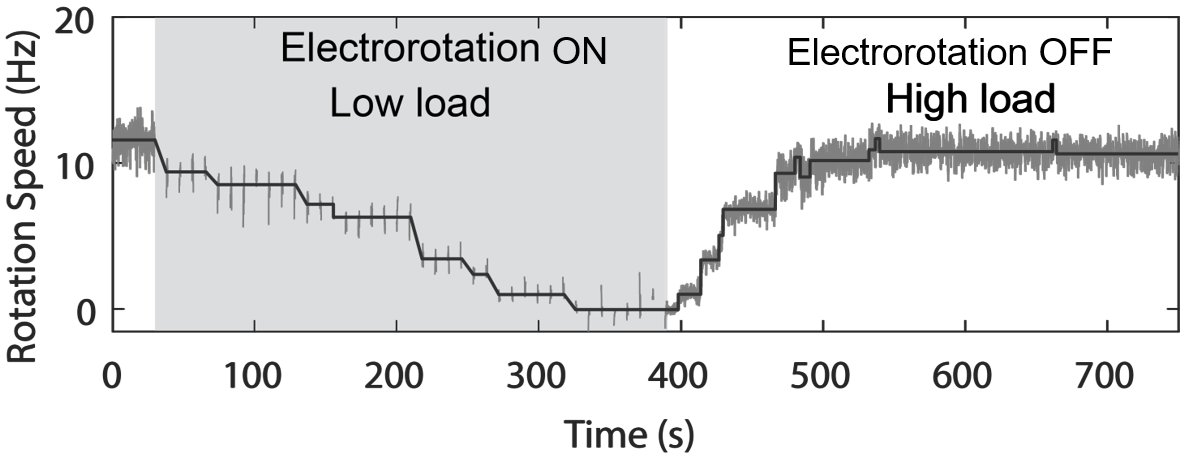
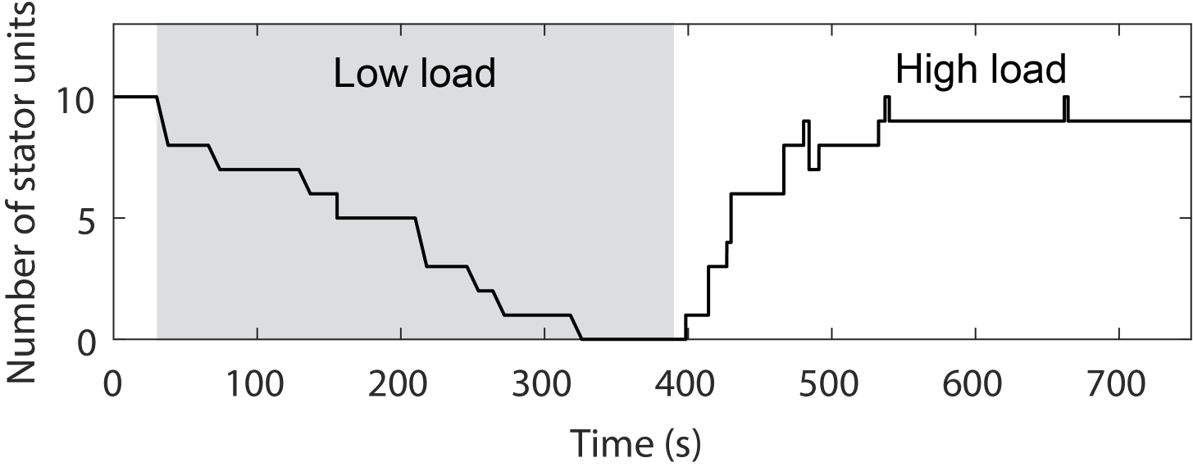
Wadhwa et al., PNAS, 2019
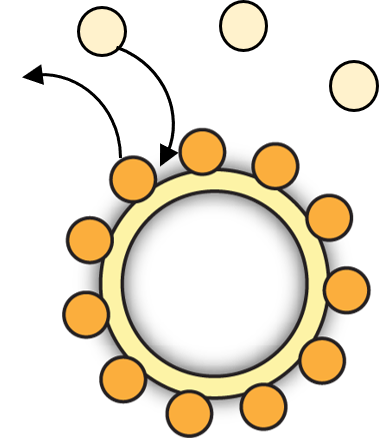
The stator remodels in response to load change
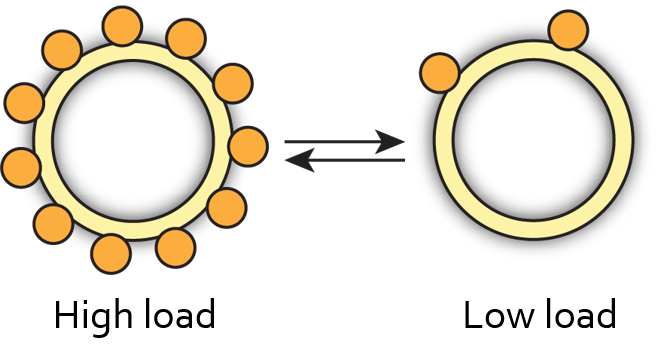
Wadhwa et al., PNAS, 2019
Lele et al., PNAS, 2013
Nord et al., PNAS, 2017
Remodeling kinetics vary with electrorotation speed
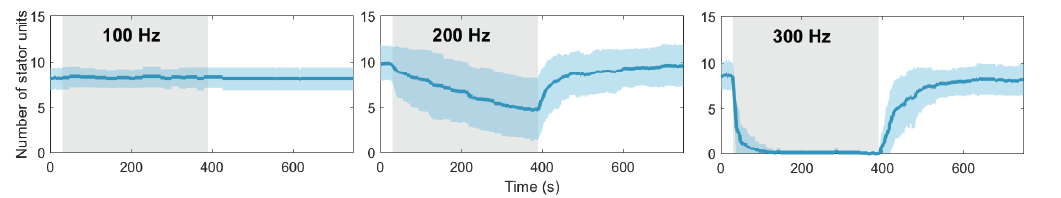
Wadhwa et al., PNAS, 2019
Remodeling kinetics vary with electrorotation speed
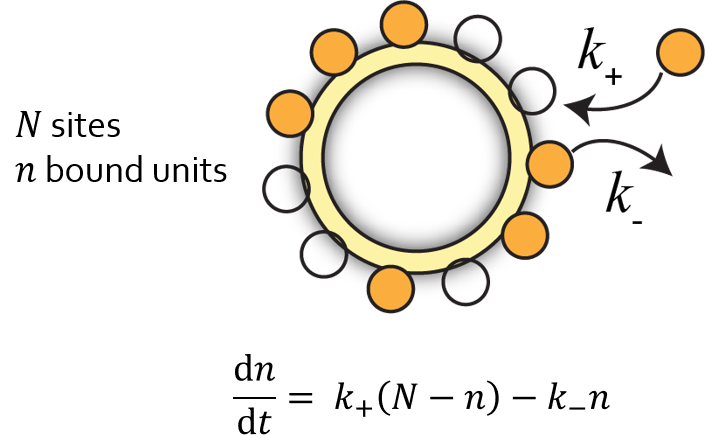
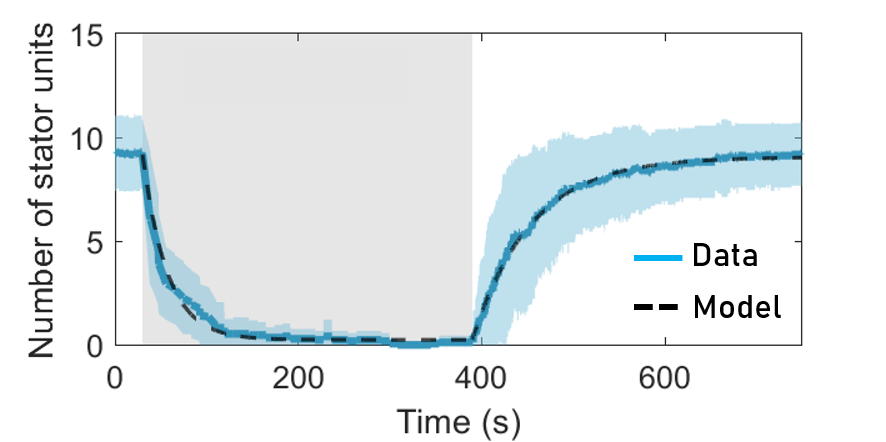
Extract the on rate ($k_+$) and the off rate ($k_-$) from the data
Wadhwa et al., PNAS, 2019
Off-rate decreases with torque
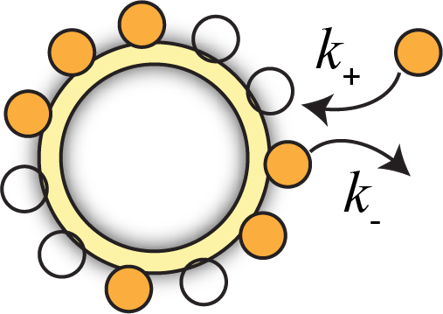
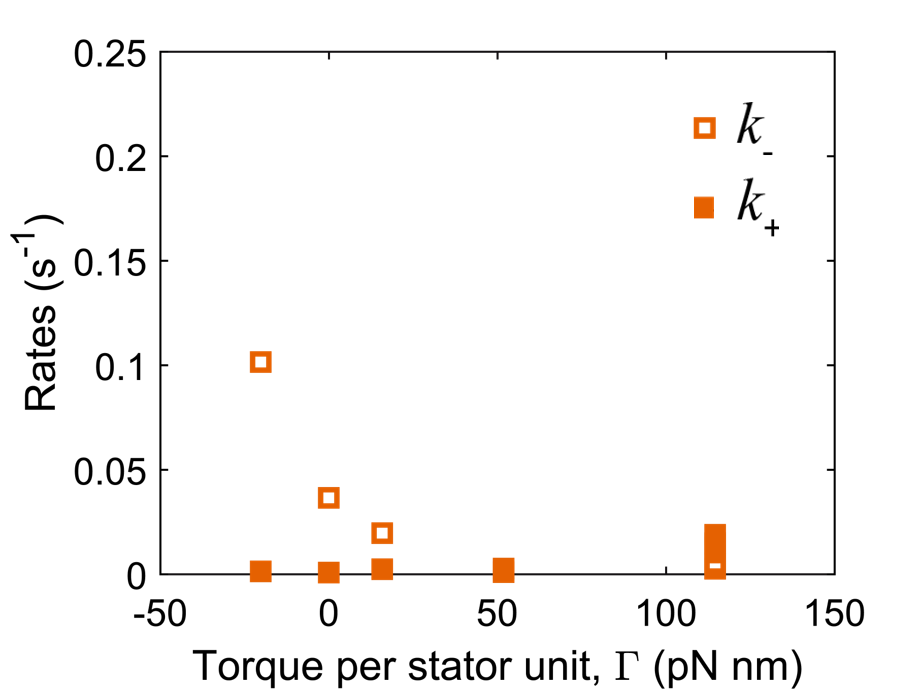
The binding gets stronger at higher torque
A passive, biophysical mechanism of mechano-adaptation
Mechanosensitive remodeling is independent of the direction of rotation
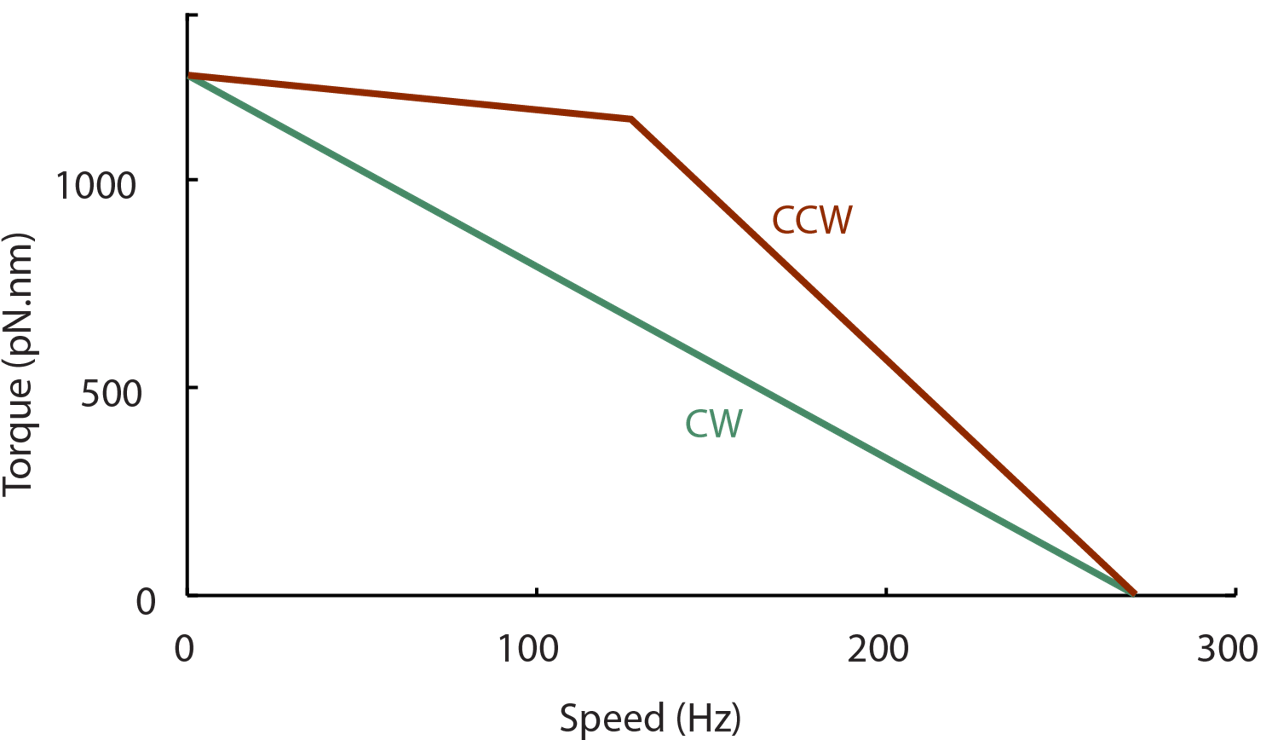
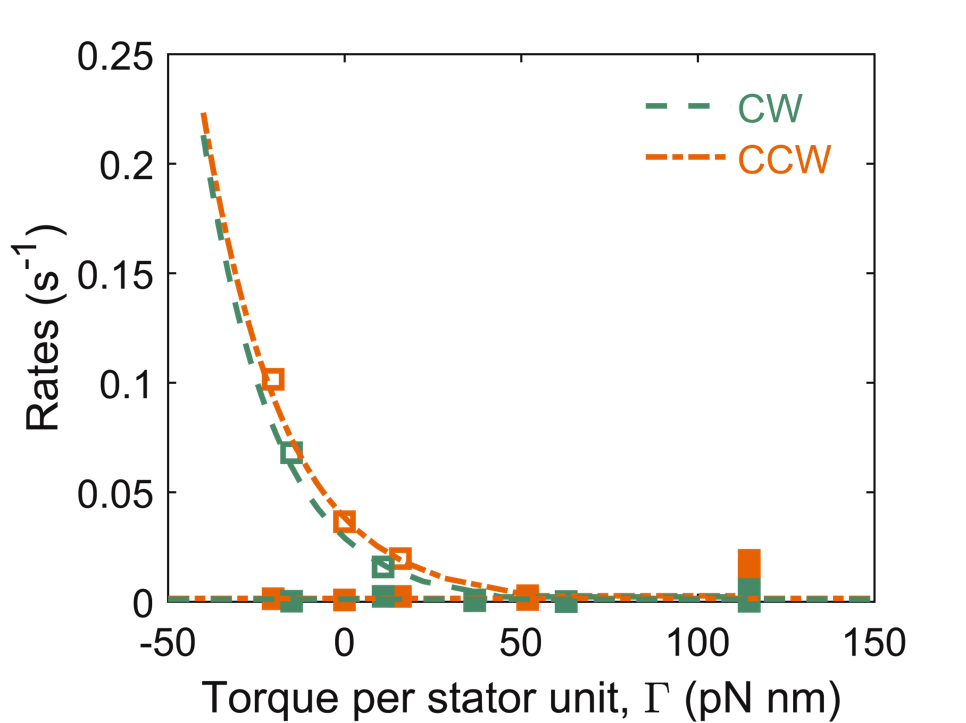
Torque is the main parameter that governs stator remodeling
Wadhwa et al., BioRxiv, 2021
Chen and Berg, Biophys. J., 2000
Yuan et al., PNAS, 2010
Cars and bacteria use different approaches

Cars adapt the transmission while bacteria adapt the engine itself
Take home


Bacterial motors adapt to changing loads by remodeling themselves.
Torque governs motor remodeling by tuning the binding kinetics.
Molecular machines are not static, fixed structures, but flexible, dynamic, and responsive.
References:
Wadhwa, Phillips, and Berg, 2019,
PNAS 116: 11764-11769
Wadhwa, Tu, and Berg, 2021,
bioRxiv 2021.01.19.427295
Acknowledgements
Collaborators
Howard Berg (Harvard)
Yuhai Tu (IBM)
Rob Phillips (Caltech)
Ethan Garner (Harvard)
Nicholas Taylor (U. Copenhagen)
Marc Erhardt (Humboldt U.)
K99/R00: GM134124
